Read
Edit
History
Notify
Share
PAW Chain
PAW Chain is a blockchain network with a tri-layer architecture to enhance scalability, speed, and flexibility. It supports various decentralized applications and tools and offers an ecosystem for efficient on-chain and off-chain interactions. [1]
Overview
PAW Chain is a blockchain network that prioritizes scalability, performance, and security while fostering decentralization and innovation. It provides infrastructure for high-frequency transactions and supports the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, offering developers tools and ensuring users control their digital assets.
The platform integrates advanced technologies to enhance interoperability and sustainability, implements robust security measures, and promotes community collaboration through decentralized governance. PAW Chain emphasizes transparency, equitable reward distribution, and ongoing research to address blockchain limitations and support long-term growth. [2]
Features
Cross Program Library (CPL)
The Cross Program Library (CPL) is an integral part of the PAW Chain ecosystem, comprising on-chain programs developed for the tri-layer parallel runtime environment. These programs are tested against PAW Swap's implementation of the tri-layer architecture and deployed on its mainnet.
CPL facilitates interoperability across various implementations of the tri-layer architecture, ensuring compatibility as PAW Chain adoption grows. Its design emphasizes flexibility and portability, with the community actively supporting updates and patches to maintain consistent functionality across platforms. [3]
PawJS
PawJS is a scripting control language developed for PAW Chain's Layer 1 infrastructure upgrade. It aims to simplify smart contract and decentralized application (dApp) development. Scheduled for release in Q4 2024, PawJS is designed to be more accessible and user-friendly than Solidity, reducing complexity and streamlining the deployment process.
The language features an intuitive syntax and enhanced readability to make development more efficient and minimize errors. Comprehensive documentation supports developers in quickly adopting PawJS and effectively utilizing its functionalities. PawJS includes built-in libraries and tools for common contract features, supports secure coding practices, and ensures compatibility with blockchain standards while leveraging PAW Chain's strengths. This upgrade is expected to lower development barriers, enhance network efficiency, and empower the creation of diverse dApps, positioning PAW Chain for future growth and scalability. [4]

Tri-layer Architecture
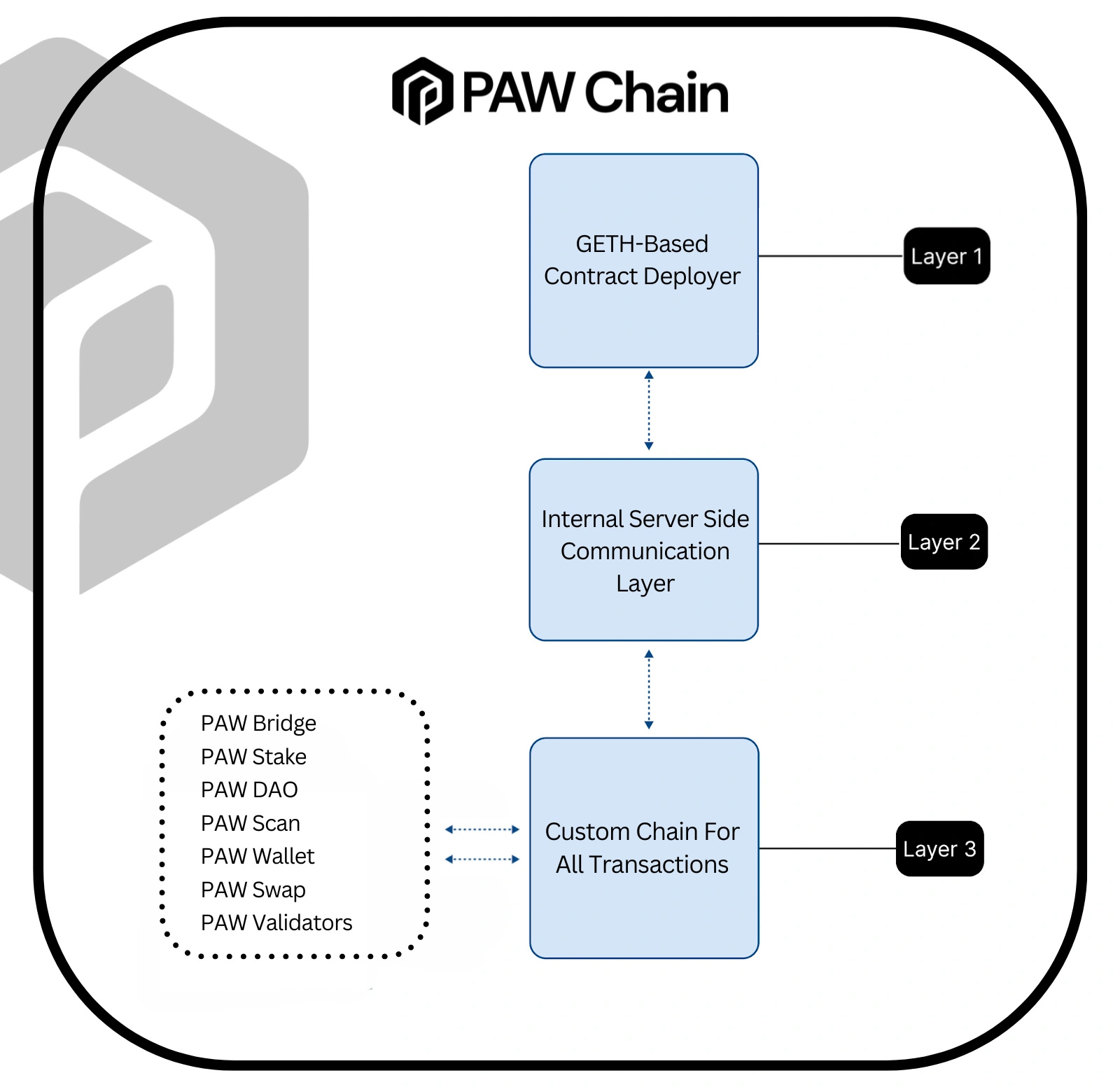
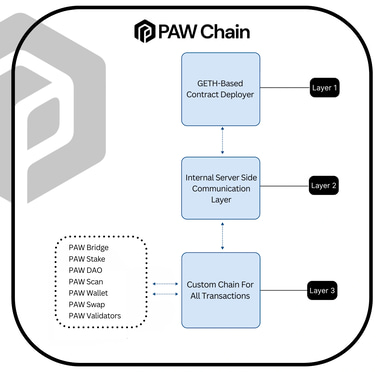
PAW Chain's tri-layer architecture integrates on-chain and off-chain processes to enhance blockchain scalability, speed, and adaptability. It addresses challenges in traditional systems by separating functions across layers and optimizing performance for specific tasks.
The architecture supports staking through DAO-linked contracts, connects to tools like the Paw Faucet via Web3, and includes a communication layer to improve internal server operations. It also facilitates custom blockchains for individual transactions, enhancing efficiency and scalability. Applications such as PAW Bridge, PAW Scan, PAW Wallet, PAW Swap, and the Validator Dashboard operate within this ecosystem.
Key advantages include increased scalability through Layer 3 handling high-frequency transactions, faster processing with reduced latency, and a modular design for flexible integration across diverse use cases. PAW Chain provides a scalable and adaptable blockchain platform with high performance and efficient functionality. [5]
Cross Stitching
PAW Chain employs a cross-stitching methodology to enhance blockchain data accuracy through a three-step redundant failure prevention system. Validators are divided into three sub-levels: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. Each block undergoes multiple verification stages to ensure data integrity.
Before block submission, two out of three validator levels verify pre-block data. During submission, two additional validators are randomly selected to verify the accuracy of the submitted block data, ensuring distinct validators handle different roles. Three validators are involved in proposing, submitting, and confirming each block, with one validator from the current block participating in pre-block and post-block confirmations. The other validators are selected from the previous block's set.
Five validators review each block, with three directly coordinating with blockchain data. The system ensures every block is confirmed twice, mitigating the risk of manipulation by malicious nodes through consistent corrections. Random validator selection further bolsters security, and the nine-cross structure maintains a safety margin even at minimum node levels. This approach ensures robust and reliable blockchain operations. [6]
Technology
PAW Swap
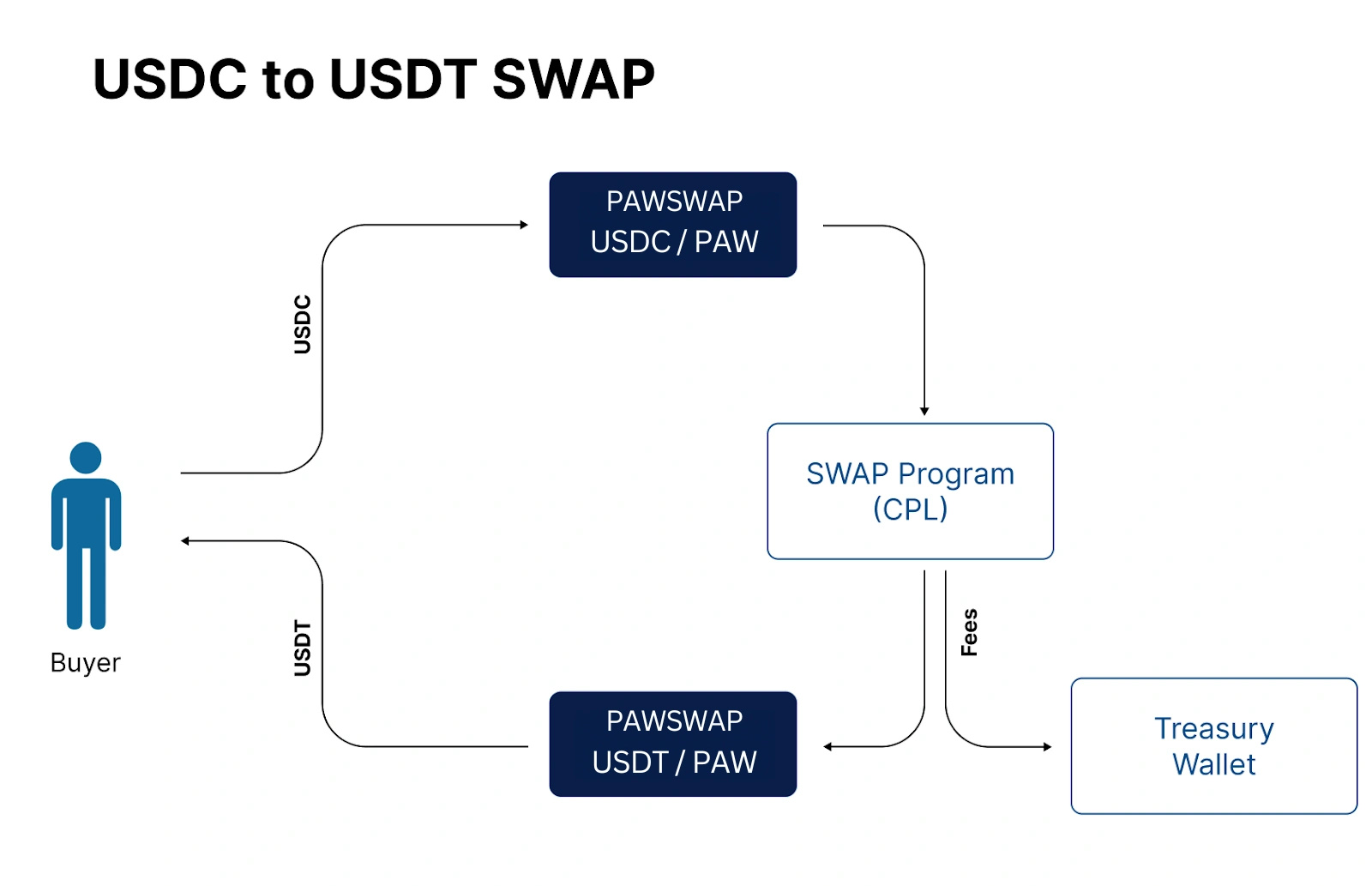
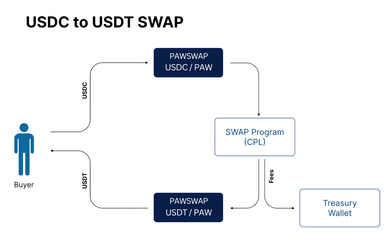
PAW Swap enables users to exchange tokens within their wallets, offering a way to adjust holdings based on investment goals and market conditions. Users select their current tokens and swap them for desired tokens, with the option to review potential transaction fees before finalizing.
The swap process involves a total fee of 0.5%, split evenly. Half is allocated to the treasury (60%) and developers (40%), while the other half is distributed among liquidity pool participants based on their contributions. Liquidity pools, managed through smart contracts, allow token trading and reward participants with liquidity provider (LP) tokens representing their shares. These tokens can be redeemed for assets in the pool and a portion of the trading fees, with share percentages displayed on the platform. [7]
PAW Wallet
PAW Wallet introduces personalized .paw usernames, offering a simpler alternative to traditional wallet addresses within the PAW Chain ecosystem. These usernames enhance accessibility by enabling users to send and receive tokens through recognizable and memorable identifiers, reducing the complexity of blockchain interactions and the potential for errors. Businesses and individuals can also use .paw usernames to establish a distinct identity on the platform.
Users can register and manage their desired usernames through the PAW Wallet app, with each username linked to a specific wallet address. These usernames, stored on the blockchain, provide verifiable ownership and can be transferred as needed. Fully integrated with PAW Chain services, .paw usernames offer compatibility across the ecosystem and can be adopted by third-party applications to enhance functionality. [8]
Multisig Wallet
The multisig feature in PAW Wallet enhances asset management by requiring approval from 5 to 9 participants for transactions, increasing security and reducing reliance on a single point of failure. Designed for organizations and collaborative projects, it supports shared management and joint decision-making, offering configurable settings and robust approval mechanisms for improved accountability and control. [8]
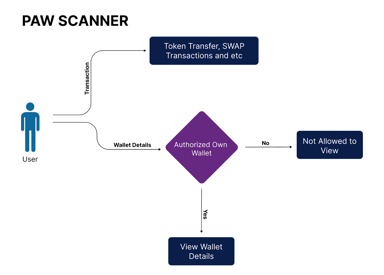
PAW Scanner
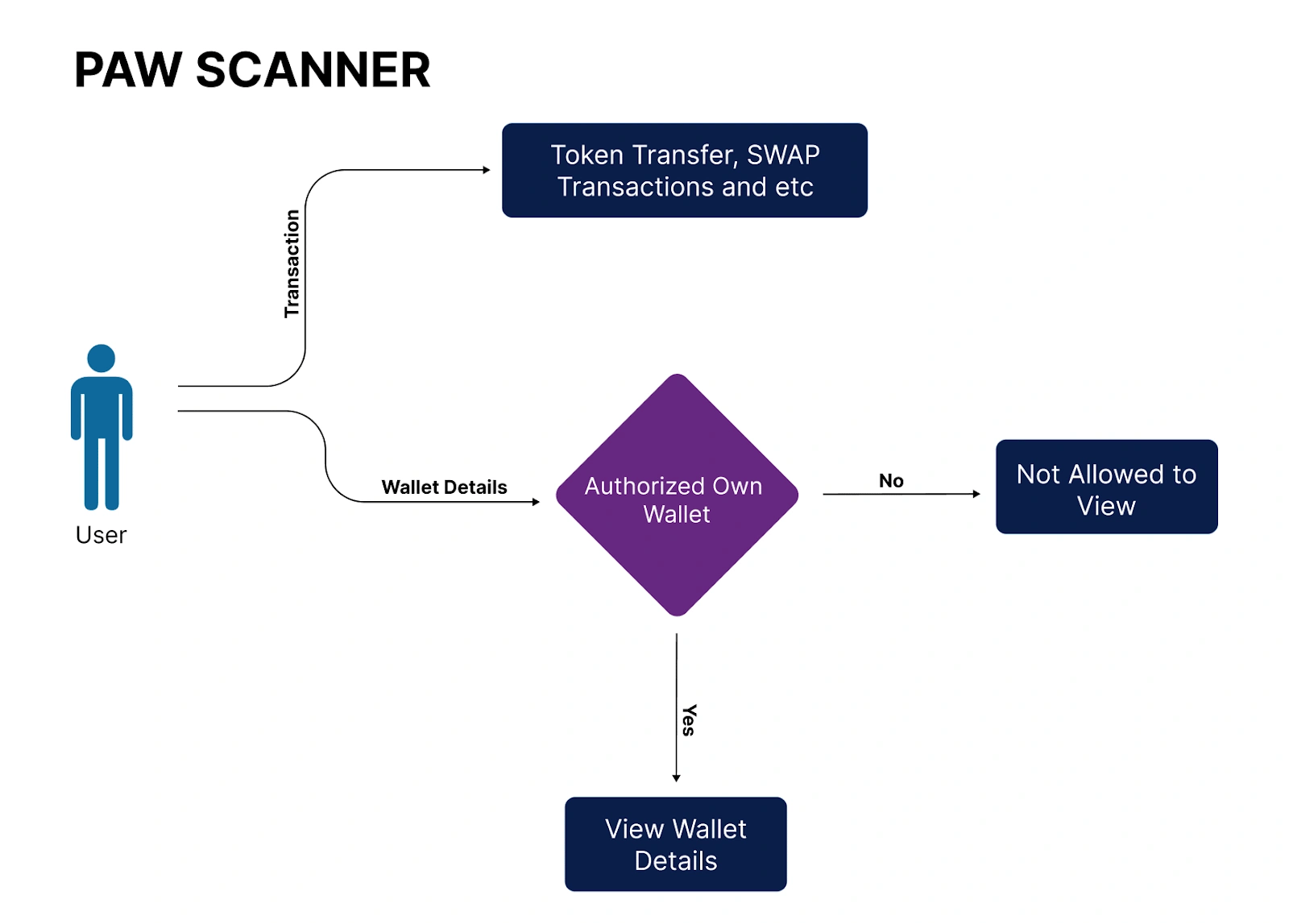
PAW Scanner is a tool within PAW Chain designed to analyze and track transactions and data across its blockchain network, enhancing transparency and security. Utilizing decentralized networks improves the efficiency and sustainability of e-currency exchanges.
It provides visibility into transaction data through real-time monitoring, using advanced algorithms to ensure transparency and accuracy. At Layer 1, it tracks transactions and asset movements through smart contract interactions, offering insights for developers. Layer 2 enables seamless cross-ledger interactions and centralized coordination for improved transparency. Layer 3 optimizes high-frequency transactions and asset coordination, increasing data processing and validation efficiency.
PAW Scanner features real-time monitoring and auditing, ensuring coherent control of transactional elements. Its analytics and reporting capabilities enhance network security by detecting fraud and anomalies through AI-driven strategies. Despite its advanced functionality, it maintains a user-friendly interface for straightforward navigation and efficient monitoring. [9]
PAW Bridge
PAW Bridge facilitates connectivity between PAW Chain and other blockchains, enabling users to access assets and services across multiple networks. This integration enhances PAW's functionality, broadens its usability, and improves the overall blockchain experience by allowing seamless asset movement and interaction across platforms.
The bridge's owner function is managed through a multi-signature wallet with nine KYC-verified signatories, ensuring robust oversight. Validator-managed authorized functions are secured within server environments, with plans to transition to a dedicated application for enhanced security.
Security measures include a bridge-out delay during the Beta phase on the L3 mainnet, which adds a validation layer for transactions exiting the PAW Chain to external networks. This safeguard protects user funds and enhances security while the platform develops further. [10]
PAW
The PAW Coin is the central asset in the ecosystem, designed with a 0% tax and deflationary characteristics. With a fixed supply, $PAW's utilities aim to reduce this supply over time, ensuring its long-term value increases. On PAW Chain, $PAW will serve as the native asset of the Layer 1 blockchain, similar to native assets on Ethereum, Solana, and other networks.
Additionally, $PAW will be represented as wPAW, a wrapped version akin to wETH, with a 1:1 ratio to PAW Coin. This approach preserves the total supply of PAW Coins (1 Quadrillion). PAW Coin gains cross-chain compatibility by adopting this model, existing on networks like Ethereum, Solana, Tron, and BNB as wPAW while maintaining its value. [11] [12]
Partnerships
Fireblocks
Gate.io
Bare Knuckle Fighting Championship
CoinCover
StealthEX
NovaDAX
Donorship
Bitkan
HashAI
Etherland
PAW Chain
Feedback
Did you find this article interesting?
Twitter Timeline
Loading
Media

REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]